Juniper to MikroTik – a new series


Previously, I’ve written a number of articles that compared syntax between Cisco and MikroTik and have received some great feedback on them.
As such, I decided to begin a series on Juniper to MikroTik starting with MPLS and L3VPN interop as it related to a project I was working on last year.
In the world of network engineering, learning a new syntax for a NOS can be overwhelming if you need a specific set of config in a short timeframe. The command structure for RouterOS can be a bit challenging if you are used to Juniper CLI commands.
If you’ve worked with Juniper gear and are comfortable with how to deploy that vendor, it is helpful to draw comparisons between the commands, especially if you are trying to build a network with a MikroTik and Juniper router.
Lab Overview
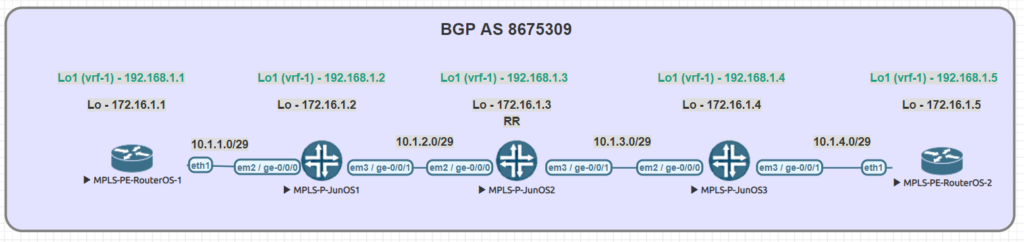
The lab consists of (3) Juniper P routers and (2) MikroTik PE routers. Although we did not get into L3VPN in this particular lab, the layout is the same.
A note on route-targets
It seems that the format of the route-target has some bearing on this being successful. Normally i’ll use a format like 8675309:1 but in this case, I had some interop issues with making that work so we used dotted decimal.
Some of the results when searching seem to suggest that platforms like Juniper and Cisco reverse the RT string in the packet while MikroTik uses it in sequential order
To work around that, the format we used was the same forwards and backwards – 1.1.1.1:1
MPLS and VPNv4 use case
MPLS is often used in service provider and data center networks to provide multi-tenancy.
VPNv4 specifically allows for separate routing tables to be created (VRFs) and advertised via BGP using the VPNv4 address family.
This address family relies on MPLS to assign a VPN label and route target as an extended community to the route which keeps it isolated from routes in other VRFs.
Practical Use
Many service provider networks rely on Juniper for the edge and core roles.
However, increasingly, ISPs want to save money on last mile and smaller aggregation points.
MikroTik is an effective choice for more simplistic MPLS capabilities as it’s inexpensive and interops with Juniper.
This creates a variety of low cost deployment options as a manged CE router, GPON aggregation in the last mile, managed CE for enterprise customers….and so on.
Command comparison
| Juniper command | MikroTik Command |
|---|---|
| > show ldp neighbor | mpls ldp neighbor print |
| > show mpls interface | mpls ldp interface print |
| > show route table mpls.0 | mpls forwarding-table print |
| > show ldp database | mpls remote-bindings print |
| > show ldp database | mpls local-bindings print |
| > show mpls label usage label-range | mpls print |
| > show ldp overview | mpls ldp print |
| # set interfaces ge-0/0/0 unit 0 family mpls # set protocols mpls interface ge-0/0/0.0 # set protocols ldp interface ge-0/0/0.0 | /mpls ldp interface add interface=ether1 |
| { inherited from loopback } | /mpls ldp set enabled=yes lsr-id=10.1.1.3 |
Testing connectivity
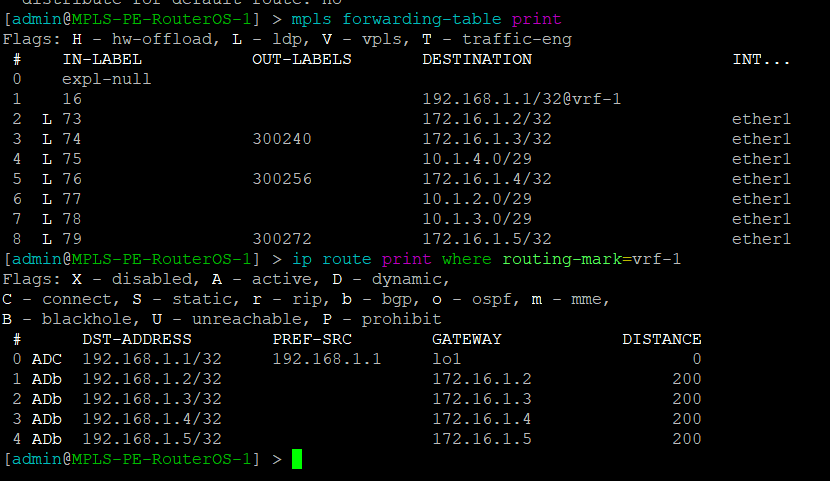
MikroTik – mpls forwarding table and vrf routes
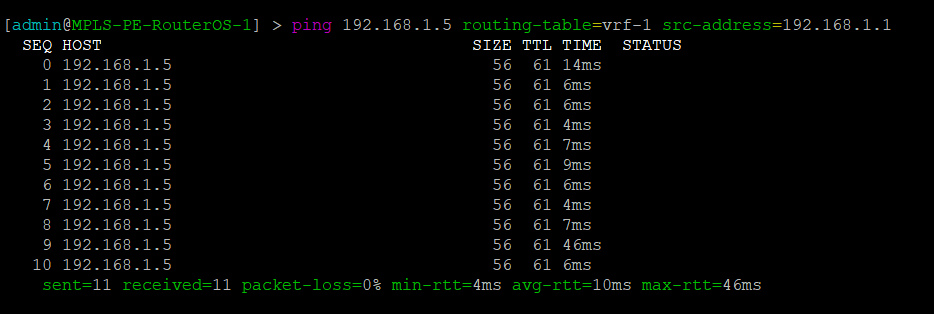
MikroTik – Ping PE2 through Juniper MPLS network
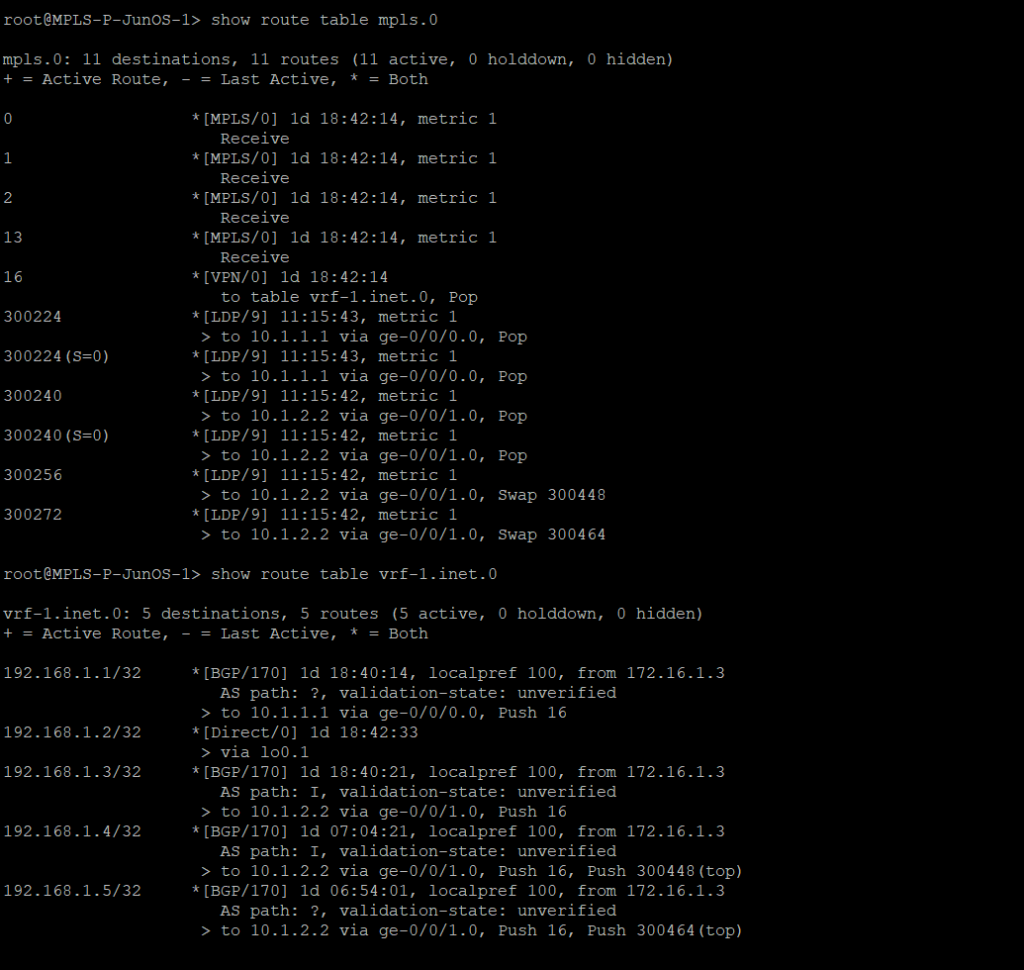
Juniper – mpls forwarding table and vrf routes
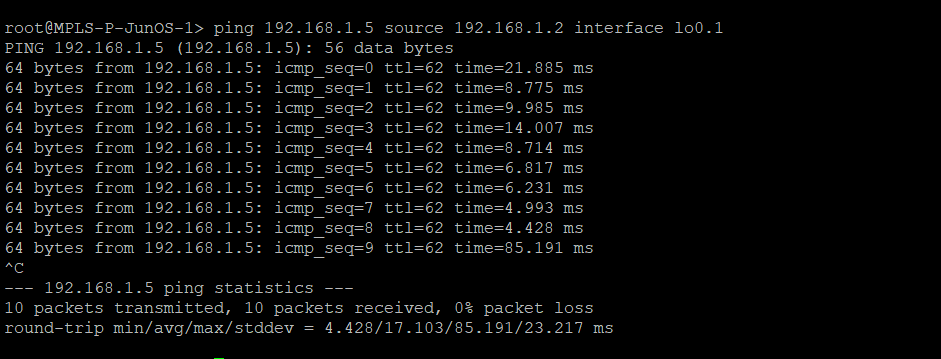
Juniper – Ping PE2 from Juniper MPLS network
Router configs
MPLS-PE-RouterOS-1
/interface bridge
add name=lo0
add name=lo1
/interface wireless security-profiles
set [ find default=yes ] supplicant-identity=MikroTik
/routing bgp instance
set default as=8675309
/ip address
add address=10.1.1.1/29 interface=ether1 network=10.1.1.0
add address=192.168.1.1 interface=lo1 network=192.168.1.1
add address=172.16.1.1 interface=lo0 network=172.16.1.1
/ip dhcp-client
add disabled=no interface=ether1
/ip route vrf
add export-route-targets=1.1.1.1:1 import-route-targets=1.1.1.1:1 interfaces=\
lo1 route-distinguisher=1.1.1.1:1 routing-mark=vrf-1
/mpls ldp
set enabled=yes lsr-id=172.16.1.1 transport-address=172.16.1.1
/mpls ldp interface
add interface=ether1
/routing bgp instance vrf
add redistribute-connected=yes routing-mark=vrf-1
/routing bgp peer
add address-families=ip,vpnv4 name=peer1 remote-address=172.16.1.3 remote-as=\
8675309 update-source=lo0
/routing ospf network
add area=backbone network=10.1.1.0/29
add area=backbone network=172.16.1.1/32
/system identity
set name=MPLS-PE-RouterOS-1
MPLS-PE-RouterOS-2
/interface bridge add name=lo0 add name=lo1 /interface wireless security-profiles set [ find default=yes ] supplicant-identity=MikroTik /routing bgp instance set default as=8675309 /ip address add address=10.1.4.2/29 interface=ether1 network=10.1.4.0 add address=192.168.1.5 interface=lo1 network=192.168.1.5 add address=172.16.1.5 interface=lo0 network=172.16.1.5 /ip dhcp-client add disabled=no interface=ether1 /ip route vrf add export-route-targets=1.1.1.1:1 import-route-targets=1.1.1.1:1 interfaces=lo1 route-distinguisher=1.1.1.1:1 routing-mark=vrf-1 /mpls ldp set enabled=yes lsr-id=172.16.1.5 transport-address=172.16.1.5 /mpls ldp interface add interface=ether1 /routing bgp instance vrf add redistribute-connected=yes routing-mark=vrf-1 /routing bgp peer add address-families=ip,vpnv4 name=peer1 remote-address=172.16.1.3 remote-as=8675309 update-source=lo0 /routing ospf network add area=backbone network=10.1.4.0/29 add area=backbone network=172.16.1.5/32 /system identity set name=MPLS-PE-RouterOS-2
MPLS-P-JunOS-1
version 14.1R1.10;
system {
host-name MPLS-P-JunOS-1;
root-authentication {
encrypted-password "$1$kj9Pva8c$R0knN0l873H.UaBUUNYA00"; ## SECRET-DATA
}
syslog {
user * {
any emergency;
}
file messages {
any notice;
authorization info;
}
file interactive-commands {
interactive-commands any;
}
}
}
interfaces {
ge-0/0/0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.1.1.2/29;
}
family mpls;
}
}
ge-0/0/1 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.1.2.1/29;
}
family mpls;
}
}
lo0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 172.16.1.2/32;
}
}
unit 1 {
family inet {
address 192.168.1.2/32;
}
}
}
}
routing-options {
router-id 172.16.1.2;
route-distinguisher-id 172.16.1.2;
autonomous-system 8675309;
}
protocols {
mpls {
traffic-engineering mpls-forwarding;
interface ge-0/0/0.0;
interface ge-0/0/1.0;
}
bgp {
group rr {
type internal;
local-address 172.16.1.2;
family inet-vpn {
unicast;
}
neighbor 172.16.1.3 {
peer-as 8675309;
}
}
}
ospf {
traffic-engineering;
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface ge-0/0/0.0;
interface ge-0/0/1.0;
interface lo0.0;
}
}
ldp {
interface ge-0/0/0.0;
interface ge-0/0/1.0;
}
}
routing-instances {
vrf-1 {
instance-type vrf;
interface lo0.1;
route-distinguisher 1.1.1.1:1;
vrf-target target:1.1.1.1:1;
vrf-table-label;
}
}MPLS-P-JunOS-2
version 14.1R1.10;
system {
host-name MPLS-P-JunOS-2;
root-authentication {
encrypted-password "$1$g6tJMNPd$f35BMnnPgit/YLshrXd/L1"; ## SECRET-DATA
}
services {
ssh;
}
syslog {
user * {
any emergency;
}
file messages {
any notice;
authorization info;
}
file interactive-commands {
interactive-commands any;
}
}
}
interfaces {
ge-0/0/0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.1.2.2/29;
}
family mpls;
}
}
ge-0/0/1 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.1.3.1/29;
}
family mpls;
}
}
lo0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 172.16.1.3/32;
}
}
unit 1 {
family inet {
address 192.168.1.3/32;
}
}
}
}
routing-options {
router-id 172.16.1.3;
route-distinguisher-id 172.16.1.3;
autonomous-system 8675309;
}
protocols {
mpls {
traffic-engineering mpls-forwarding;
interface ge-0/0/0.0;
interface ge-0/0/1.0;
}
bgp {
group rr {
type internal;
local-address 172.16.1.3;
family inet-vpn {
unicast;
}
cluster 1.1.1.1;
neighbor 172.16.1.2 {
peer-as 8675309;
}
neighbor 172.16.1.1 {
peer-as 8675309;
}
neighbor 172.16.1.3 {
peer-as 8675309;
}
neighbor 172.16.1.4 {
peer-as 8675309;
}
neighbor 172.16.1.5 {
peer-as 8675309;
}
}
}
ospf {
traffic-engineering;
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface ge-0/0/0.0;
interface ge-0/0/1.0;
interface lo0.0;
}
}
ldp {
interface ge-0/0/0.0;
interface ge-0/0/1.0;
}
}
policy-options {
policy-statement import-vrf1 {
term import-term-connected {
from protocol direct;
then accept;
}
term term-reject {
then reject;
}
}
}
routing-instances {
vrf-1 {
instance-type vrf;
interface lo0.1;
route-distinguisher 1.1.1.1:1;
vrf-target target:1.1.1.1:1;
vrf-table-label;
}
}MPLS-P-JunOS-3
version 14.1R1.10;
system {
host-name MPLS-P-JunOS-3;
root-authentication {
encrypted-password "$1$kj9Pva8c$R0knN0l873H.UaBUUNYA00"; ## SECRET-DATA
}
syslog {
user * {
any emergency;
}
file messages {
any notice;
authorization info;
}
file interactive-commands {
interactive-commands any;
}
}
}
interfaces {
ge-0/0/0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.1.3.2/29;
}
family mpls;
}
}
ge-0/0/1 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.1.4.1/29;
}
family mpls;
}
}
lo0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 172.16.1.4/32;
}
}
unit 1 {
family inet {
address 192.168.1.4/32;
}
}
}
}
routing-options {
router-id 172.16.1.4;
route-distinguisher-id 172.16.1.4;
autonomous-system 8675309;
}
protocols {
mpls {
traffic-engineering mpls-forwarding;
interface ge-0/0/0.0;
interface ge-0/0/1.0;
}
bgp {
group rr {
type internal;
local-address 172.16.1.4;
family inet-vpn {
unicast;
}
neighbor 172.16.1.3 {
peer-as 8675309;
}
}
}
ospf {
traffic-engineering;
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface ge-0/0/0.0;
interface ge-0/0/1.0;
interface lo0.0;
}
}
ldp {
interface ge-0/0/0.0;
interface ge-0/0/1.0;
}
}
routing-instances {
vrf-1 {
instance-type vrf;
interface lo0.1;
route-distinguisher 1.1.1.1:1;
vrf-target target:1.1.1.1:1;
vrf-table-label;
}
}