What is MLAG?
Multi-Chassis Link Aggregation Group or MLAG is an idea that’s been around for a while.
It allows for the ability to form LACP channels across multiple physical switches.
Wikipedia shows a few different topology examples here
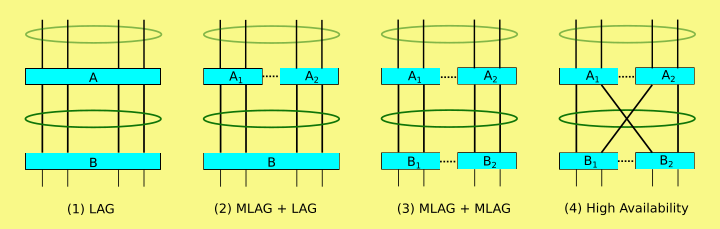
Vendor implementations are proprietary but the idea of MLAG was first mentioned in 802.1AX-2008 in 2008.
It first started to become popular in data center networking in the late 2000s
What makes the addition of MLAG to MikroTik’s RouterOS feature set notable is that it lowers the barrier to entry for this particular feature.
CRS 3xx switches are very inexpensive (starting at $149 USD) and may very well be the lowest cost MLAG capable hardware available on the market.
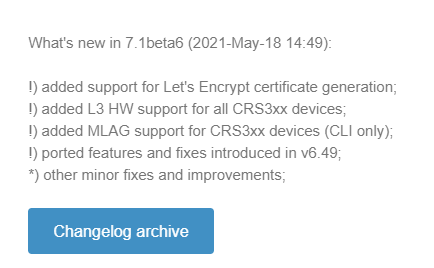
Introduced in 7.1beta6
MLAG has been asked for by the MikroTik community a number of times and the most active feature request thread started here in 2020:
new feature request MLAG!!! – MikroTik
MikroTik added several version 7 beta releases in 2021 and included MLAG for all CRS 3xx series switches in 7.1beta6 on May 18th, 2021.
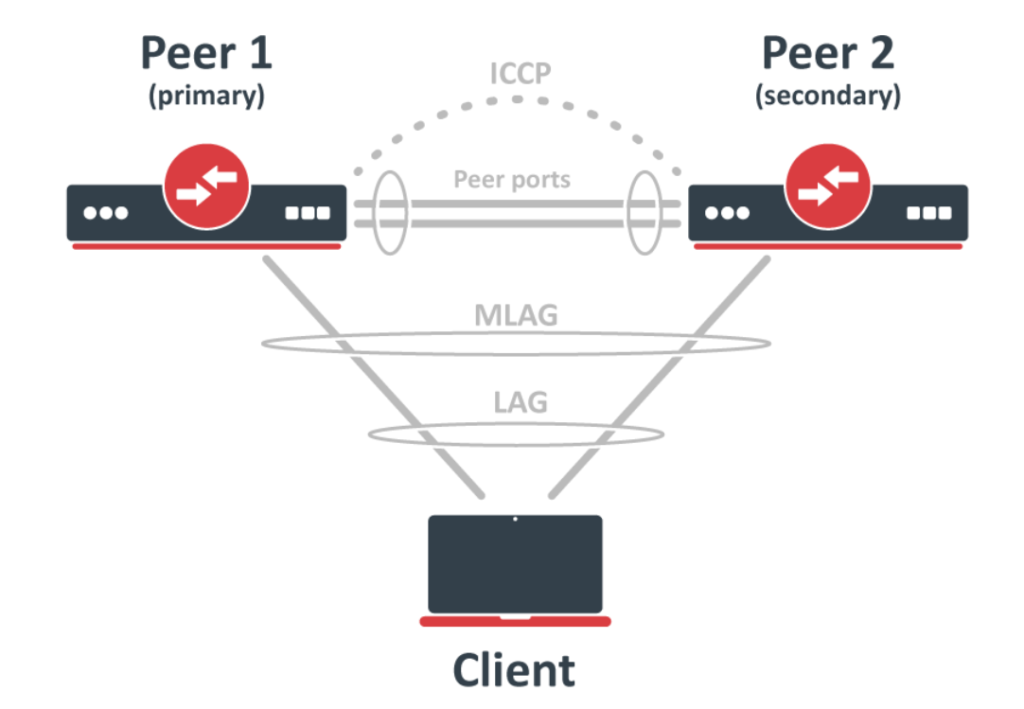
Overview of protocol requirements
MLAG is fairly consistent across vendors with the need for a link between physical devices that manages the MLAG groups. In MikroTik, these are called peer ports which facilitate the ICCP.
Here are a few terms for MikroTik MLAG:
ICCP (Inter Chassis Control Protocol). – Responsible for determining active/secondary switches and maintaining and updating the bridge table between physical switches.
Peer port – An interface that will be used as a peer port. Both peer devices use inter-chassis communication over the peer ports to establish MLAG and update the host table. The Peer port should be isolated on a different untagged VLAN using a pvid setting. The Peer port can be configured as a bonding interface.
System-id – The lowest MAC address between both peer bridges will be used as the system-id. This system-id is used for (R)STP bridge identifier.
Active-role – The peer with the lowest bridge MAC address will be acting as a primary device. The primary device is responsible for sending the correct LACP system ID on all MLAG ports.
mlag-id – An integer from 0 to 4294967295, it is used to set the MLAG ID for bonding interfaces. The same MLAG ID should be used on both peer devices to successfully create a single MLAG.
MikroTik’s requirements for ICCP and MLAG are:
- RouterOS ICCP does not require an IP configuration
- It should be isolated from the rest of the network using a dedicated untagged VLAN
- Peer ports can also be configured as LACP bonding interfaces
- MLAG requires enabled STP or RSTP protocol.
In order to present a single MAC address for the L2 spanning tree topology, ICCP functions on top of the peer ports to manage the MLAG/LACP system-id.
The system-id is used as the MAC address presented to the LACP client for RSTP/MSTP bridge identification.
reference for images and MLAG definitions: Multi-chassis Link Aggregation Group – RouterOS – MikroTik Documentation
Lab Example
In order to test the new MLAG functionality, we decided to setup a lab with CRS326-24S+2Q switches and CCR2004-1G-12S+2XS routers.
Below is the lab physical and logical topology.
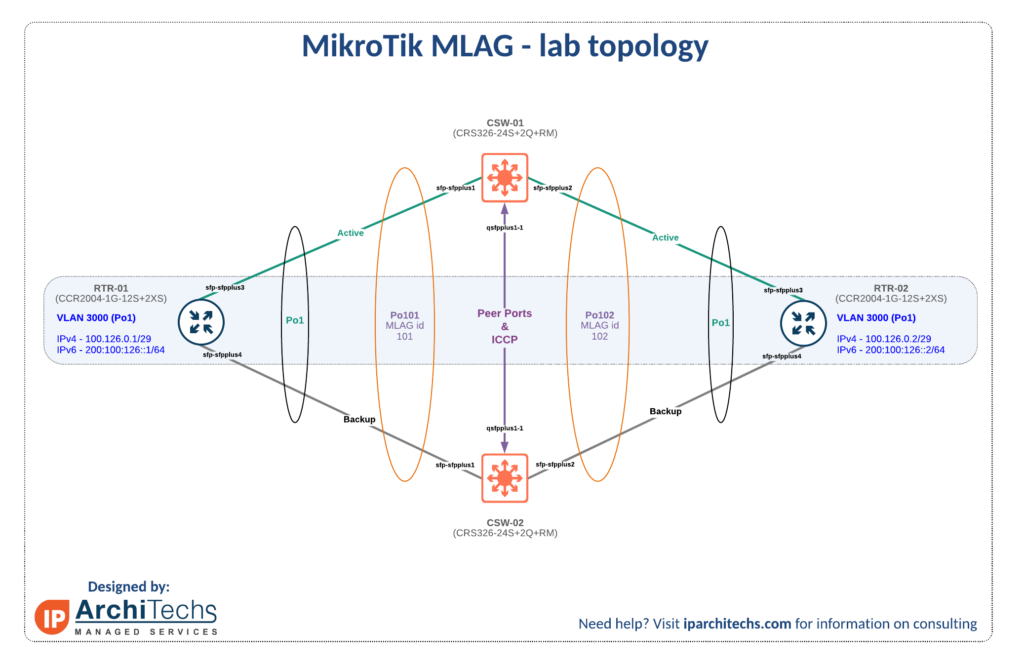
Configuring an MLAG Group
Configure Bond and MLAG ID on CSW-01
/interface bonding add mlag-id=100 mode=802.3ad name=Po1 slaves=sfp-sfpplus1
Configure Bond and MLAG ID on CSW-02
/interface bonding add mlag-id=100 mode=802.3ad name=Po1 slaves=sfp-sfpplus1
* Apply each configuration step below on both switches to complete mlag setup and mlag-id 100. *
Configure the bridge and enable VLAN filtering. Add MLAG bonded interfaces and peer port to the bridge.
/interface bridge add name=Bridge-MLAG vlan-filtering=yes /interface bridge port add bridge=Bridge-MLAG interface=Po1 add bridge=Bridge-MLAG interface=qsfpplus1-1 pvid=777
Configure a VLAN to be used over the MLAG
/interface bridge vlan add bridge=Bridge-MLAG tagged=Po1 vlan-ids=3000
Set the peer port
/interface bridge mlag set bridge=Bridge-MLAG peer-port=qsfpplus1-1
Validate the MLAG group
Show the status of the MLAG group, active and secondary ports and verify the system-id the client LACP receives
######## MLAG Switches - 2 x CRS326 ############
[admin@CSW-01] > interface/bridge/mlag/monitor
status: connected
system-id: 48:8F:5A:3A:44:BA
active-role: primary
[admin@CSW-02] > interface/bridge/mlag/monitor
status: connected
system-id: 48:8F:5A:3A:44:BA
active-role: secondary
######## NON-MLAG LACP Router ############
[admin@RTR-01] > /interface bonding monitor Po1
mode: 802.3ad
active-ports: sfp-sfpplus3,sfp-sfpplus4
inactive-ports:
lacp-system-id: 48:8F:5A:00:4F:80
lacp-system-priority: 65535
lacp-partner-system-id: 48:8F:5A:3A:44:BA
Configurations
RTR-01
/interface bridge add name=Lo0 /interface bonding add mode=802.3ad name=Po1 slaves=sfp-sfpplus3,sfp-sfpplus4 transmit-hash-policy=layer-2-and-3 /interface vlan add interface=Po1 name=vlan3000 vlan-id=3000 /routing table add fib name="" /ip address add address=100.126.0.1/29 interface=vlan3000 network=100.126.0.0 add address=100.127.0.1 interface=Lo0 network=100.127.0.1 /ipv6 address add address=200:100:126::1 interface=vlan3000 add address=200:100:127::1/128 advertise=no interface=Lo0 /system identity set name=RTR-01
RTR-02
/interface bridge add name=Lo0 /interface bonding add mode=802.3ad name=Po1 slaves=sfp-sfpplus3,sfp-sfpplus4 transmit-hash-policy=layer-2-and-3 /interface vlan add interface=Po1 name=vlan3000 vlan-id=3000 /routing table add fib name="" /ip address add address=100.126.0.2/29 interface=vlan3000 network=100.126.0.0 add address=100.127.0.2 interface=Lo0 network=100.127.0.2 /ipv6 address add address=200:100:126::2 interface=vlan3000 add address=200:100:127::2/128 advertise=no interface=Lo0 /system identity set name=RTR-02
CSW-01
/interface bridge add name=Bridge-MLAG vlan-filtering=yes /interface bonding add mlag-id=100 mode=802.3ad name=Po1 slaves=sfp-sfpplus1 add mlag-id=101 mode=802.3ad name=Po2 slaves=sfp-sfpplus2 /interface bridge mlag set bridge=Bridge-MLAG peer-port=qsfpplus1-1 /interface bridge port add bridge=Bridge-MLAG interface=Po1 add bridge=Bridge-MLAG interface=qsfpplus1-1 pvid=777 add bridge=Bridge-MLAG interface=Po2 /interface bridge vlan add bridge=Bridge-MLAG tagged=Po1,Po2 vlan-ids=3000 /system identity set name=CSW-01
CSW-02
/interface bridge add name=Bridge-MLAG vlan-filtering=yes /interface bonding add mlag-id=100 mode=802.3ad name=Po1 slaves=sfp-sfpplus1 add mlag-id=101 mode=802.3ad name=Po2 slaves=sfp-sfpplus2 /interface bridge mlag set bridge=Bridge-MLAG peer-port=qsfpplus1-1 /interface bridge port add bridge=Bridge-MLAG interface=Po1 add bridge=Bridge-MLAG interface=qsfpplus1-1 pvid=777 add bridge=Bridge-MLAG interface=Po2 /interface bridge vlan add bridge=Bridge-MLAG tagged=Po1,Po2 vlan-ids=3000 /system identity set name=CSW-02